Active Directory is an enterprise-class directory service that is scalable, built from the ground up using internet-standard technologies, and fully integrated at the operating-system level. Active Directory simplifies administration and makes it easier for users to find resources. Active Directory stores information about network components. It also is designed especially for distributed networking environments.
Features
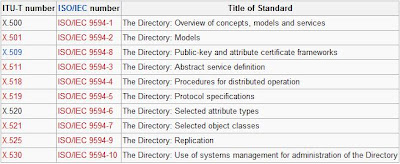
- Support for the X.500 standard for global directories
- An object-oriented storage organization, which allows easier access to information
- Support for the LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) to enable inter-directory operability
Active Directory Security Issues
- Forest and Domains
- Native Mode
- Schema
- Organizational Units (OU)
- Global Catalog
- Domain Controllers and Replication
- Domain Name System (DNS)
References